Investigating Windows Event Logs
28/06/2022 Tuesday
On Windows operating systems, the event logs store a lot of useful information about the system, users, activities and applications. The main purpose of the event logs is to provide information to administrators and users. They are structured in five levels (information, warning, error, critical, and success/failure audit). In terms of forensic analysis, this is a valuable source to understand the course of actions on a system. In this post, we went through how Windows ArtiFast analyzes "Windows Event Logs" artifact in detail.
Digital Forensics Value of Windows Event Logs
Windows event logs are important for understanding incidents that occurred on a target system. This artifact can be a valuable source of information, especially, during data leak or hacking cases. Security event logs store incidents based on the Windows operating system audit policies. On the other hand, system event logs contain the status of a device and operating system specific incidents. Application event logs track application erros, installation results and more.
Windows Event Viewer enables administrators and users to view the event logs. The tool provides filtering capabilites by time, event level and source, however, navigating through the Event Viewer can be challenging due to the amount of information presented. Therefore, text-based structured analysis of event logs may be considered a better approach. Users can identify the results and causes of cyber incidents on a system by corelating specific events on the system and focusing on specific event ids (such as 4624, 4625, and so on).
Location of Windows Event Logs
In Windows operating systems, the default location of the event logs is at
C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs
In addition, information related to the Custom logs can be found in the following registry key:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Eventlog
Structure of Windows Event Logs
Windows event log are structured in five channels:
- Application - contains information logged by applications on the system.
- Security - contains incidents related to security events according to the auditing policy of the Windows operating system. This log contains login attemps (success and failure), elevated priviledges, and more. Details of the security event logs can be increased by applying a specialized auditing policy either locally or by a GPO.
- Setup - captures incidents of installation or upgrading of the Windows operating system.
- System - contains messages generated by the Windows operating system.
- Forwarded Events - contains events which are forwarded by other computers. This event is populated if Windows Event Forwarding is enabled and the local machine is running as a central subscriber, other machines are forwarders.
Analyzing Windows Event Logs
This section discusses how to use ArtiFast Windows to analyze Windows Event Log artifact from Windows machines and
what kind of digital forensics insight we can gain from the artifact.
After you have created your case and added evidence for the investigation,
at the Artifact Selection phase, you can select Windows Event Logs artifact:
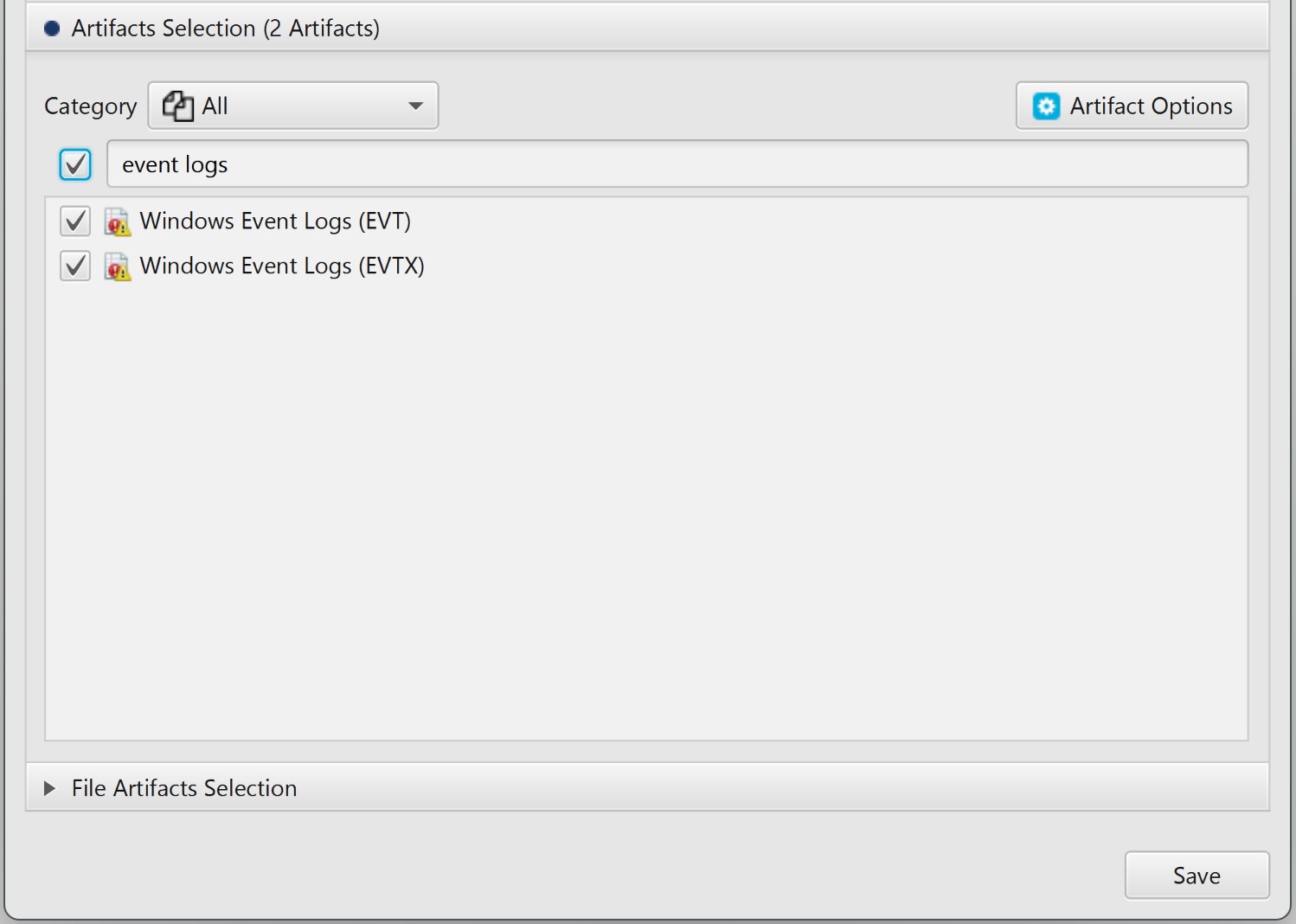
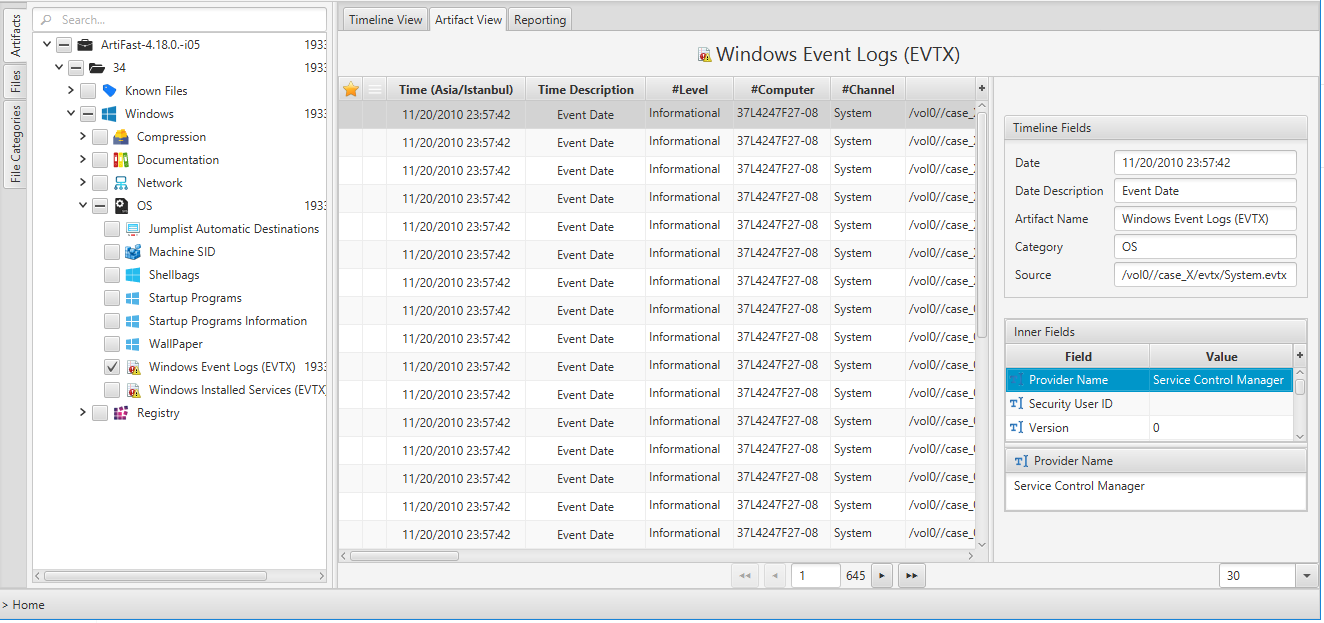
By double clicking on a specific log entry on the Artifact View, you can investigate details of the that log entry. The figure below shows the details of a Security event id 4624 (successful logon).
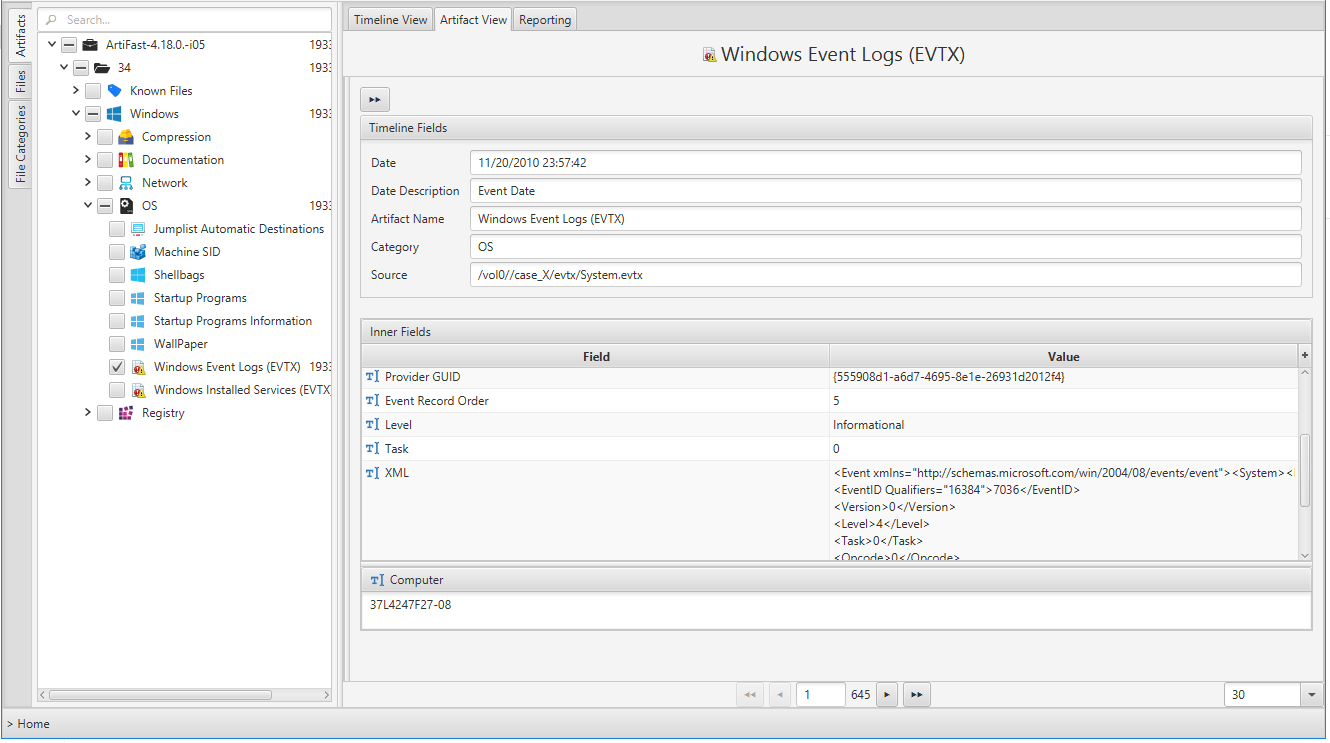
Once ArtiFast parser plugins complete processing the artifact for analysis, it can be reviewed via “Artifact View” or “Timeline View,” with indexing, filtering, and searching capabilities. Below is a detailed description of the Windows Event Logs artifact in ArtiFast software.
Windows Event Logs Artifact
The artifact contains Event Logs in Windows operating systems. The details you can view include:
- Level - Event log level/type. This can be information, warning, error, success/failure audit.
- Channel - Event log channel or category. Security, Application, System etc.
- Computer - Local system name.
- Event ID - Event identification number. By filtering according to ID we can get the important events.
- Keywords - They are used to group the event with other similar events based on the usage of the events.
- Opcode - The activity or a point within an activity that the application was performing when it raised the event.
- Provider GUID - The unique GUID for the provider. It is useful when performing research or operations on a specific provider.
- Provider Name - Name of event provider.
- Security User ID - It is used to uniquely identify a security principal or security group.
- Task - Identifies the type of recorded event log. Application developers can define custom task categories for providing additional details.
- Event Record Order - Order of the event in the main event category.
- Located At - File offset location of the specific event.
- Event Record ID - Event record identification number in the main category.
- XML - XML view of the event,
- Record Length - Lenght of the event.
For more information or suggestions please contact: asmaa.elkhatib@forensafe.com
