Solving African Falls Challenge with ArtiFast Windows
13/08/2021 Friday
In this blog post, we will be solving a challenge designed by Cyber Defenders using ArtiFast Windows. The purpose of this challenge is to analyze the disk image acquired from the suspect’s laptop to determine whether the person in question was performing illegal activities (scenario).
After reviewing the case details, the following is a summary of the important artifacts that we need to analyze:
- Web Browser Artifacts - to investigate web browser related activity. The suspect is using three different web browsers Chrome, Brave and Edge.
- Prefetch Artifact - to investigate program execution.
- Shellbags Artifact - to investigate previously accessed folders.
- Recycle Bin Artifact - to investigate deleted files.
- PowerShell Artifact - to investigate the history of executed commands.
- USB Artifact - to investigate external devices connected to the suspect’s device.
Analyzing User Activity with ArtiFast Windows
After you have created your case and added the image for investigation, at the Artifacts Parser Selection Phase, you can either select the artifacts mentioned earlier or you can choose to run all artifacts:
Once ArtiFast parser plugins complete processing artifacts for analysis, it can be reviewed via "Artifact View" or "Timeline View", with indexing, filtering, and searching capabilities. Below is a detailed analysis of the user activities.
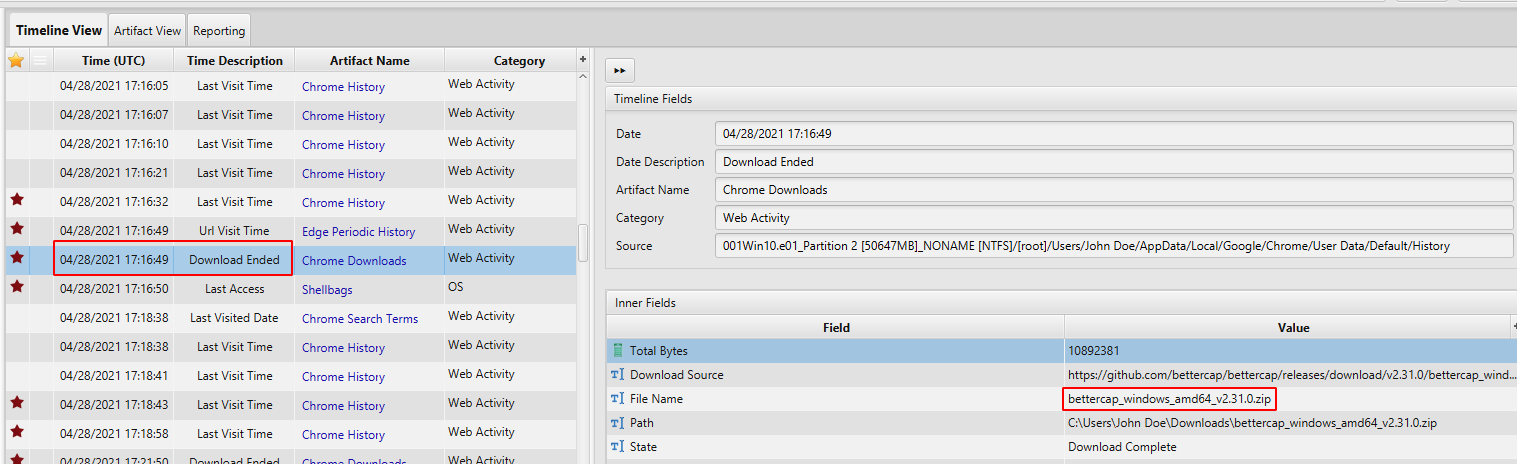
- Tools Preparation: According to Chrome Download Artifact, between 04/28/2021 17:15:05 - 04/28/2021 17:21:50, the user downloaded Nmap, bettercap and Wireshark which are known software for capturing, scanning and analyzing network traffic.
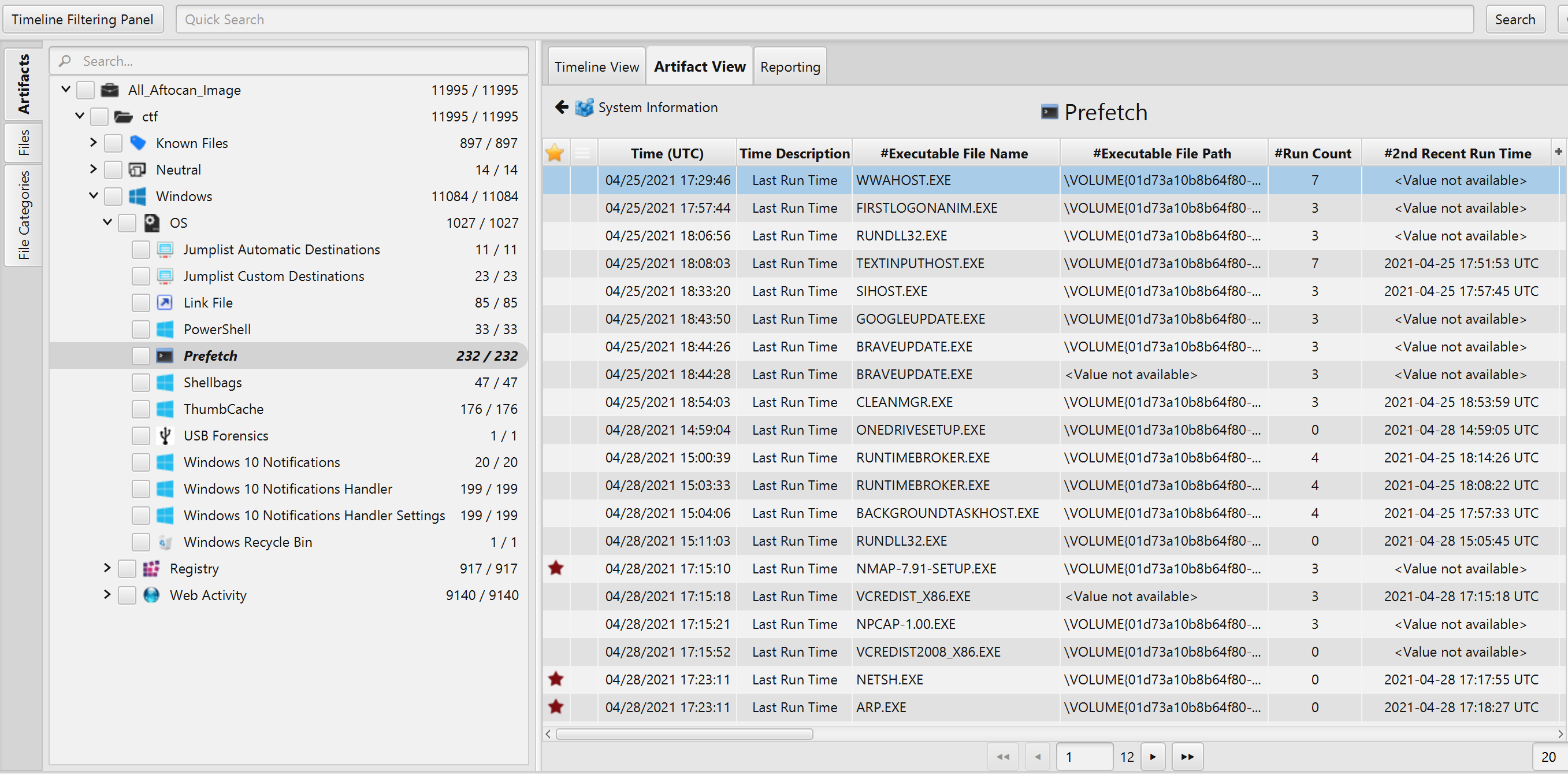
- Scanning and Sniffing the Network: According to Prefech Artifact, between 04/28/2021 17:24:05 - 04/28/2021 17:37:54, the user first run bettercap, then, Nmap and lastly Wireshark to scan the network as seen in the picture below.
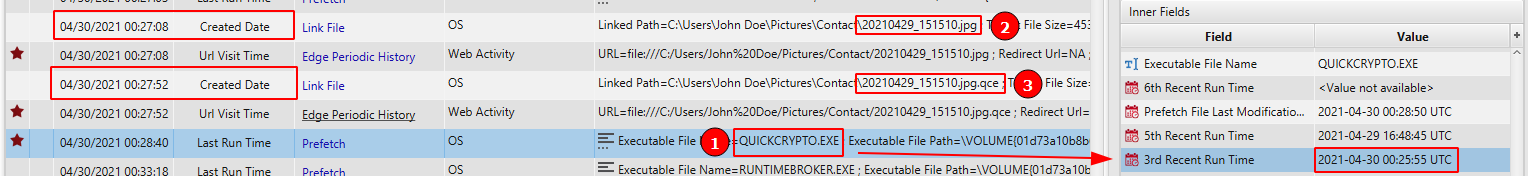
- Hiding Data: On 04/29/2021 16:44:11, John started searching for ways to hide the data. Apparently, he decided on using QucikCrypto and installed the program on the system. Then, he run the application on 2021-04-30 00:25:55 UTC to hide the data inside 20210429_151510.jpg . After execution, the file became 20210429_151510.jpg.qce.
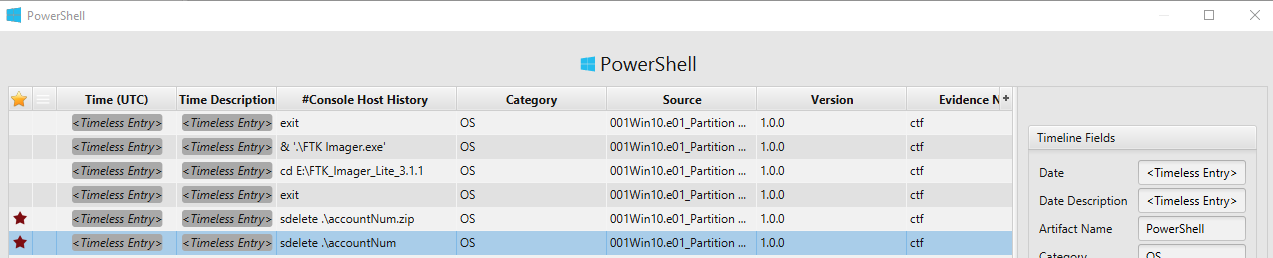
- Deleting Data: On 04/29/2021 20:45:02, John downloaded SDelete software and run it at 20:45:12. Since SDelete is a command tool utility, we can check Powershell artifact to determine which file was deleted. As seen in the picture below, John run the program against accountNum file.
- Nmap

- bettercap
- Wireshark
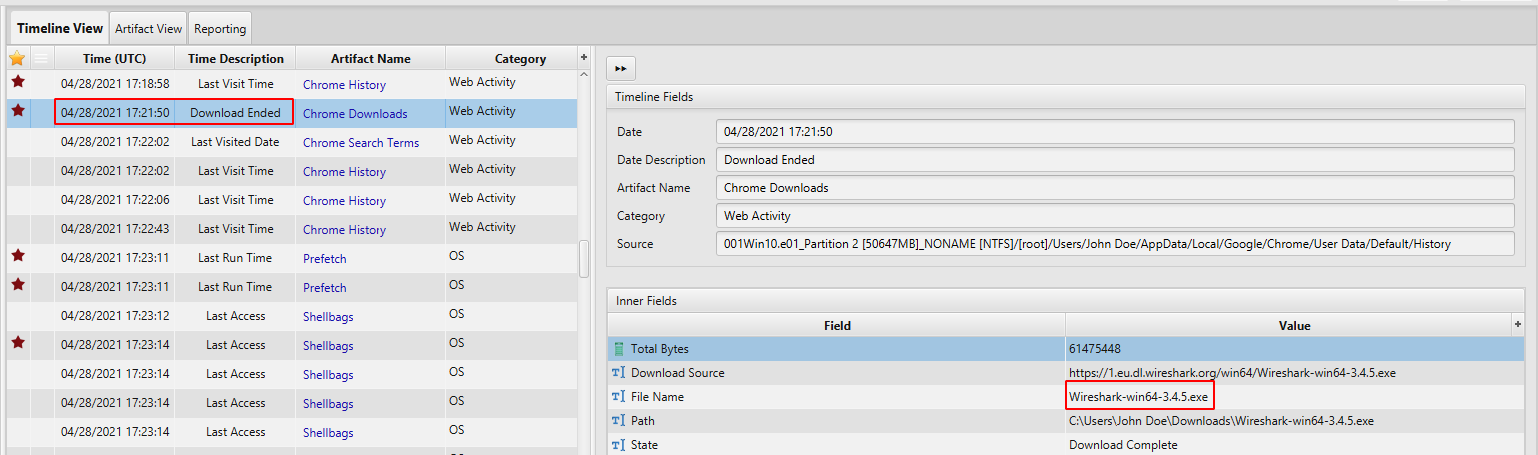
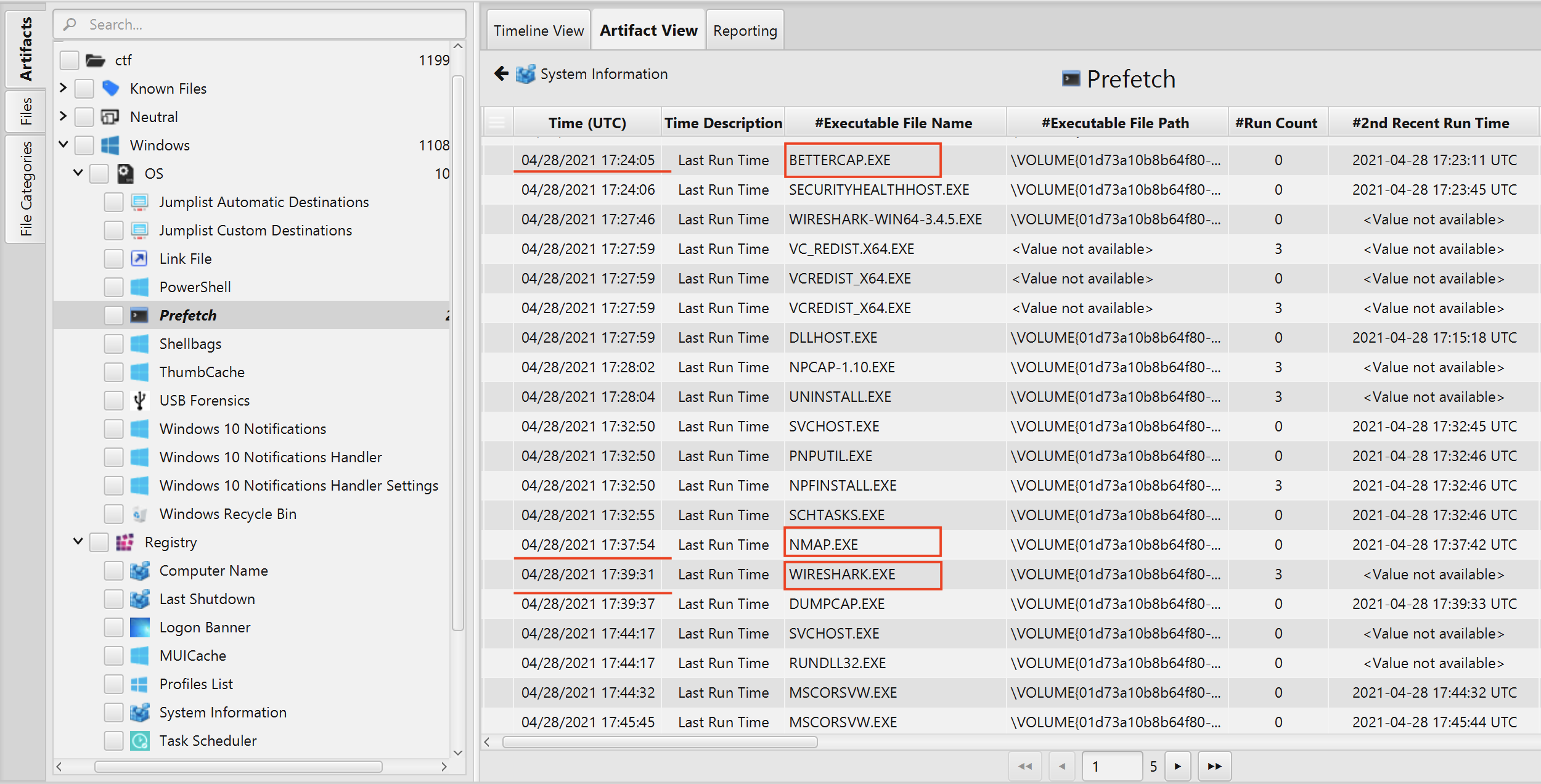
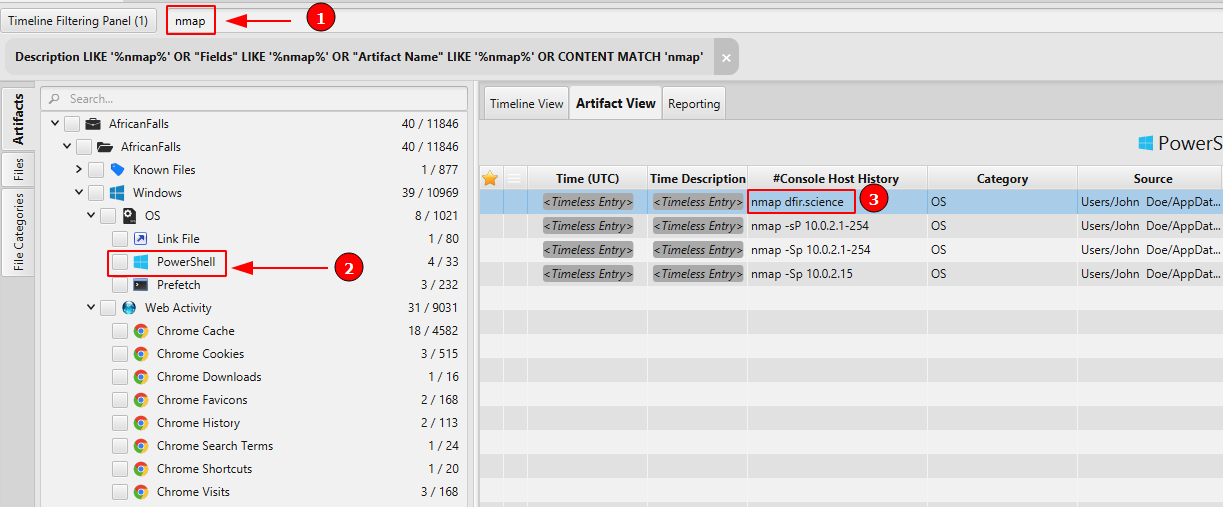
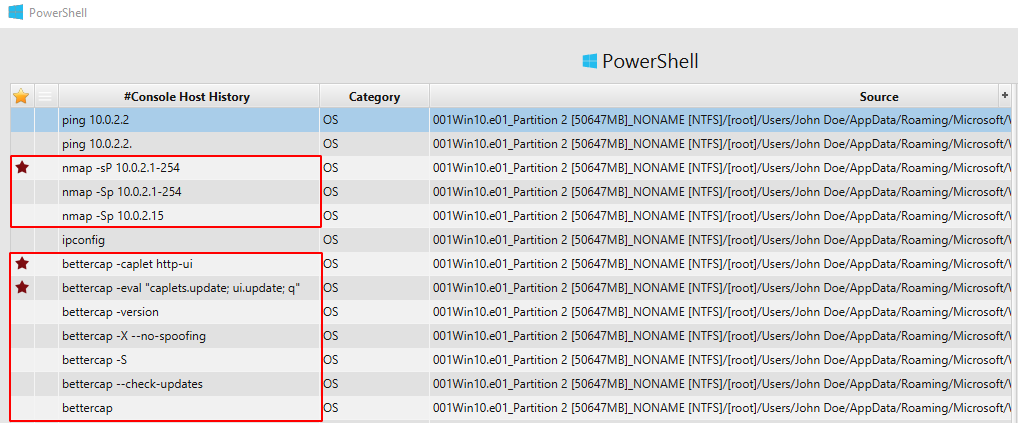
We now know that the user run bettercap, Nmap and Wireshark, however, we need to know what kind of command did he execute. In order to find the recent commands executed by John, we can check Powershell artifact.
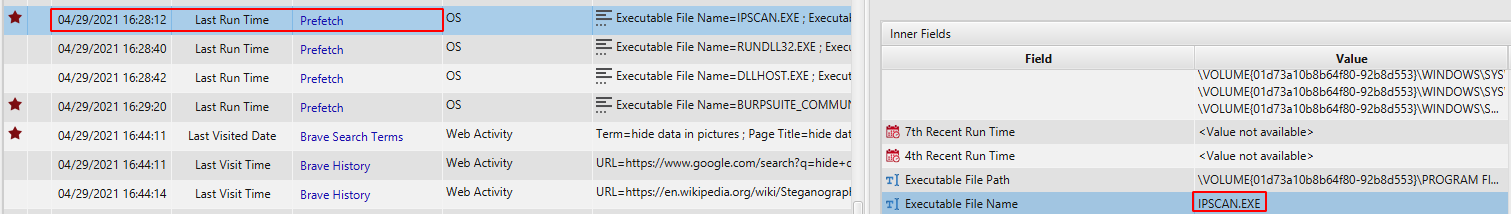
In addition, we can see that John downloaded Angry IP Scanner and he run it at 04/29/2021 16:28:12.
Timeline Analysis Summary
04/28/2021 17:15:05 - downloaded Nmap.
04/28/2021 17:16:49 - downloaded bettercap.
04/28/2021 17:21:50 - downloaded Wireshark.
04/28/2021 17:24:05 - run bettercap to sniff the network.
04/28/2021 17:37:54 - run Nmap to scan the network.
04/28/2021 17:39:31 - run Wireshark.
04/29/2021 16:03:03 - downloaded Angry IP Scanner.
04/29/2021 16:21:22 - inserted USB.
04/29/2021 16:28:12 - run Angry IP Scanner.
04/29/2021 16:46:31 - downloaded Quick Crypto software to hide data.
04/29/2021 18:19:16 - downloaded TOR browser, but did not run it.
04/29/2021 18:20:22 - downloaded password wordlist to the USB.
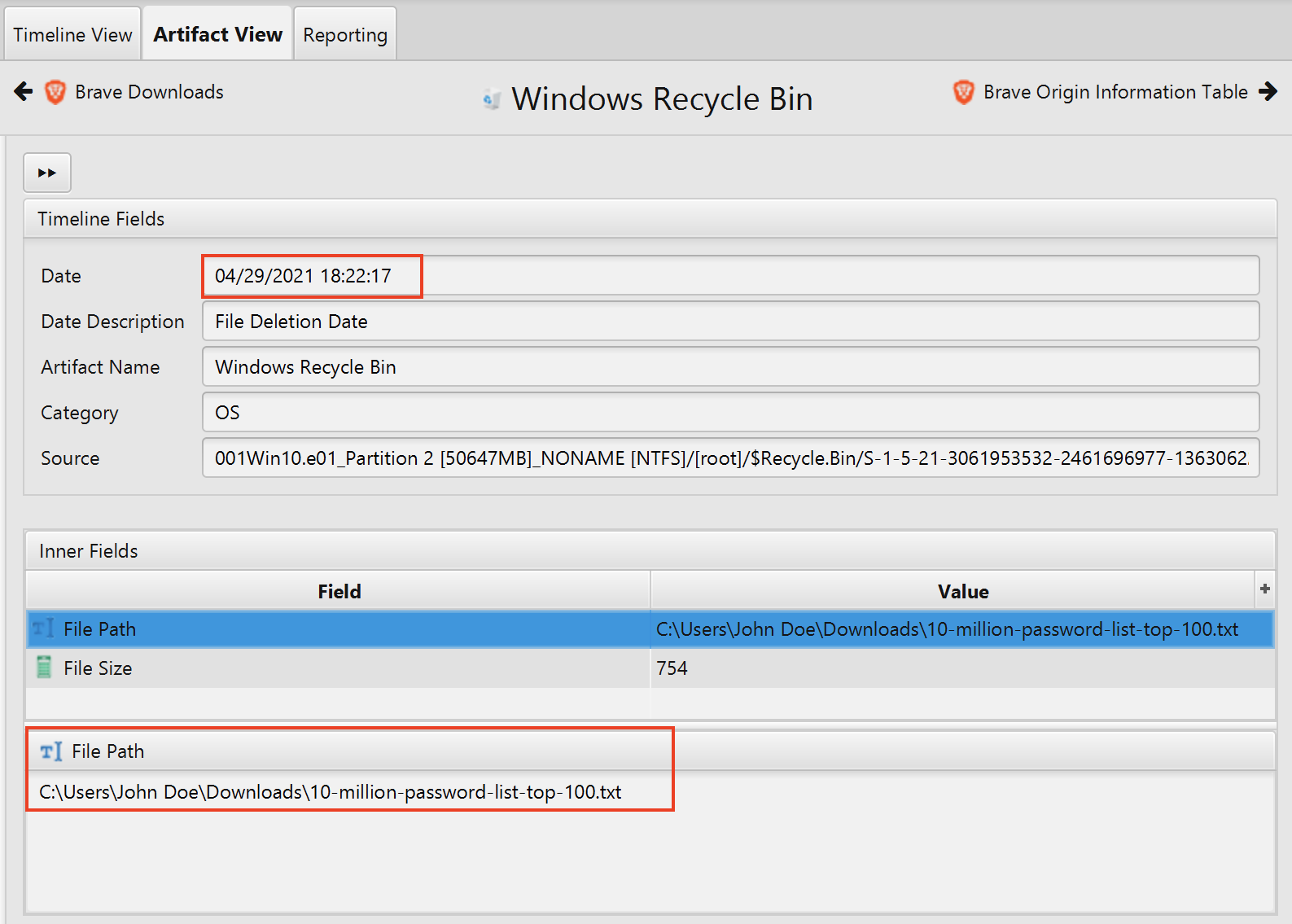
04/29/2021 18:22:17 - deleted password wordlist from download folder.
04/29/2021 20:45:02 - downloaded SDelete software.
04/30/2021 00:28:40 - run Quick Crypto to hide data inside the picture.
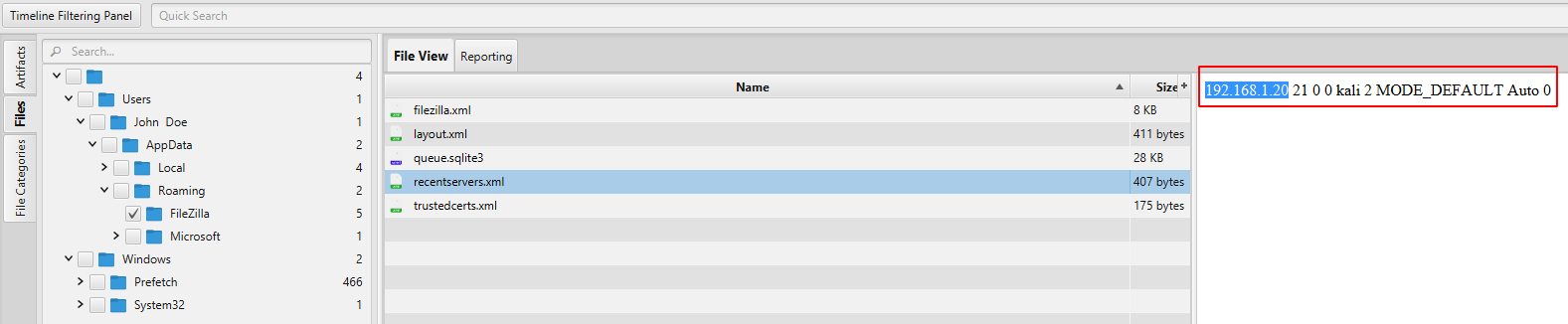
04/30/2021 01:01:09 - run filezila and accessed FTP server (192.168.1.20).
04/30/2021 01:02:42 - accessed the accountNum folder.
04/30/2021 01:08:06 - run SDelete agenst accountNum to delete it.
Challenge Questions
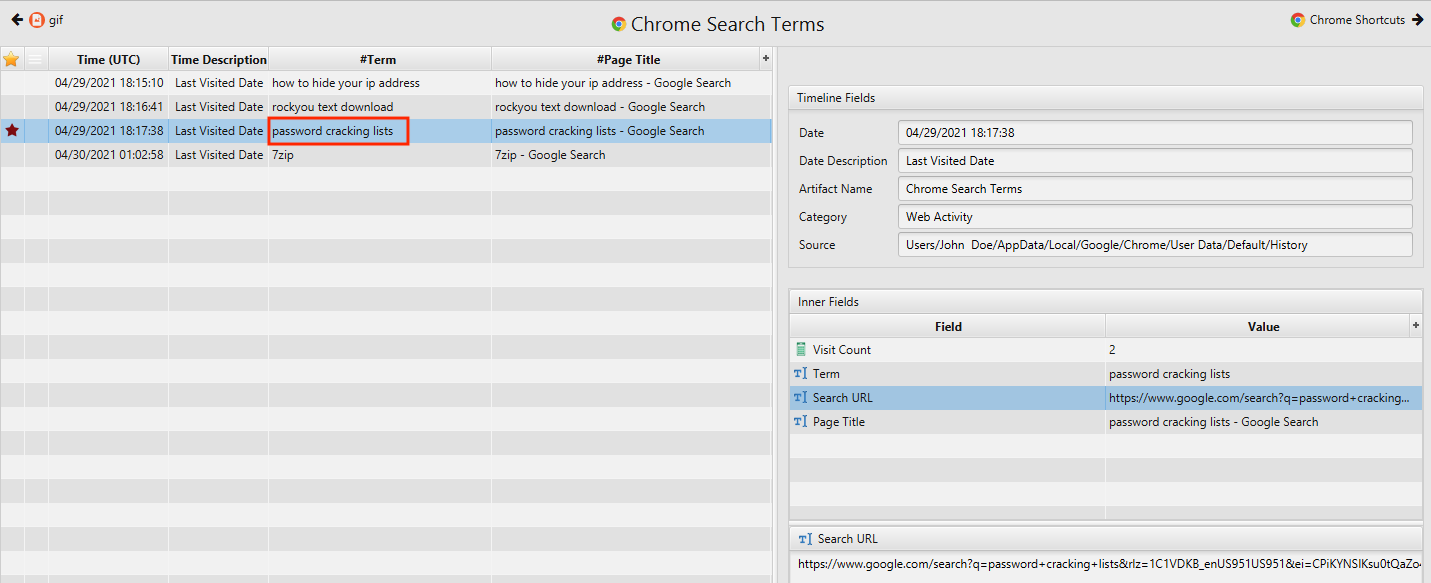
- What phrase did the suspect search for on 2021-04-29 18:17:38 UTC? (three words, two spaces in between)
The answer can be found in Chrome Search Terms artifact under the Web Activity category. The phrase is password cracking lists.
- What is the IPv4 address of the FTP server the suspect connected to?
- What date and time was a password list deleted in UTC? (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS UTC)
The answer can be found in Windows Recycle Bin artifact under the OS category.
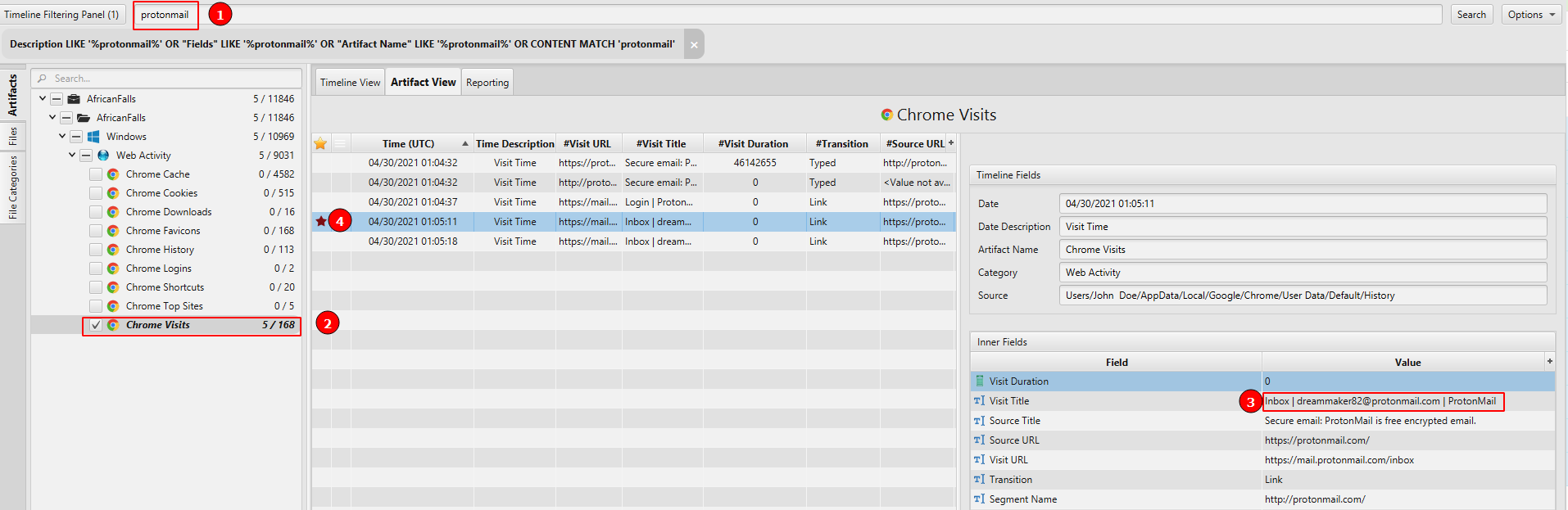
- What is the suspect's email address?
The answer can be found in Chrome Visits artifact under the Web Activity category.
- What is the FQDN did the suspect port scan?
The answer can be found in PowerShell artifact under the OS category.